What is menstruation?
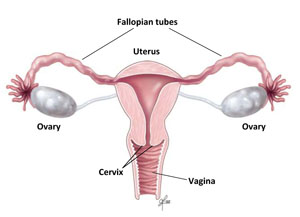
Menstruation is the monthly shedding of the lining of a woman’s uterus (more commonly known as the womb). Menstruation is also known by the terms menses, menstrual period, cycle or period. The menstrual blood—which is partly blood and partly tissue from the inside of the uterus—flows from the uterus through the cervix and out of the body through the vagina.
What is a normal menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle is a term used to describe the sequence of events that occur within a woman’s body as it prepares for the possibility of pregnancy each month. A menstrual cycle is considered to begin on the first day of a period. The average cycle is 28 days long; however, a cycle can range in length from 21 days to about 35 days.
The steps in the menstrual cycle are triggered by the rise and fall of chemicals in the body called hormones. The pituitary gland in the brain and the ovaries in the female reproductive tract manufacture and release certain hormones at certain times during the menstrual cycle that cause the organs of the reproductive tract to respond in certain ways. The specific events that occur during the menstrual cycle can be described as follows:
- The menses phase: This phase, which typically lasts from day one to day five, is the time when the lining of the uterus is actually shed out through the vagina if pregnancy has not occurred. Most women bleed for three to five days, but a period lasting only two days to as many as seven days is still considered normal.
- The follicular phase: This phase typically takes place from days six to 14. During this time, the level of the hormone estrogen rises, which causes the lining of the uterus (called the endometrium) to grow and thicken. In addition, another hormone—follicle-stimulating hormone—causes follicles in the ovaries to grow. During days 10 to 14, one of the developing follicles will form a fully mature egg (ovum).
- Ovulation: This phase occurs roughly at about day 14 in a 28-day menstrual cycle. A sudden increase in another hormone—luteinizing hormone—causes the ovary to release its egg. This event is called ovulation.
- The luteal phase: This phase lasts from about day 15 to day 28. After the egg is released from the ovary it begins to travel through the fallopian tubes to the uterus. The level of the hormone progesterone rises to help prepare the uterine lining for pregnancy. If the egg becomes fertilized by a sperm and attaches itself to the uterine wall, the woman becomes pregnant. If pregnancy does not occur, estrogen and progesterone levels drop and the thickened lining of the uterus is shed during the menstrual period.
At what age does menstruation typically begin?
Girls start menstruating at the average age of 12. However, girls can begin menstruating as early as 8 years of age or as late as 16 years of age. Women stop menstruating at menopause, which occurs at about the age of 51. At menopause, a woman stops producing eggs (stops ovulating). Menopause is defined as one year without periods, and after this time a woman can no longer become pregnant.
What are some of the symptoms of a normal menstruation?
- Moodiness
- Trouble sleeping
- Food cravings
- Cramps in the lower abdomen and back
- Bloating
- Tenderness in the breasts
- Acne
What symptoms may indicate a need to contact my doctor about my period?
Contact your doctor or healthcare provider if:
- You have not started menstruating by the age of 16
- Your period stops suddenly
- You are bleeding for more days than usual
- You are bleeding more heavily than usual
- You have severe pain during your period
- You have bleeding between periods
- You suddenly feel sick after using tampons
- You think you might be pregnant—for example, you have had sex and your period is at least five days late
- Your period has not returned within three months after stopping birth control pills and you know you are not pregnant
- You have any questions or concerns about your period or possible pregnancy
Reference: Clevelandclinic
Written by: Omojo Emeje




